Gitlab CI Integration
Introduction
In the GitOps section, we have introduced how to integrate KCL with GitOps. In this section, we will continue to provide sample solutions for KCL and CI integrations. We hope to implement the end-to-end application development process by using containers, Continuous Integration (CI) for generation, and GitOps for Continuous Deployment (CD). In this scheme, we use a Flask application and Gitlab CI as examples.
Note: You can use any containerized application and different CI systems such as Github Actions, Jenkins CI, etc. in this solution.
The overall workflow is as follows:
- Develop application code and submit it to the Gitlab repository to trigger CI.
- Gitlab generate container images from application code and push them to the
docker.iocontainer registry. - Gitlab CI automatically synchronizes and updates the KCL manifest deployment file based on the version of the container image in the docker.io container registry.
How to
We put the application source code and infrastructure deployment code in different repos, which can be maintained by different roles to achieve the separation of concerns.
1. Get the Example
- Get the application code
git clone https://gitlab.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo.git/
cd flask-demo
This is a web application written in Python. We can use the Dockerfile in the application directory to generate a container image of this application, and also use Gitlab CI to automatically build a image named flask_demo, the CI configuration is as follows
stages:
- publish
- deploy
publish:
stage: publish
image:
name: cnych/kaniko-executor:v0.22.0
entrypoint: [""]
script:
- echo "{\"auths\":{\"$CI_REGISTRY\":{\"username\":\"$CI_REGISTRY_USER\",\"password\":\"$CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD\"}}}" > /kaniko/.docker/config.json
- /kaniko/executor --context $CI_PROJECT_DIR --dockerfile ./Dockerfile --destination $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:$CI_COMMIT_SHA
only:
- main
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: cnych/kustomize:v1.0
before_script:
- git remote set-url origin https://gitlab.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo
- git config --global user.email "gitlab@git.local"
- git config --global user.name "GitLab CI/CD"
# Install KCL
- wget -q https://kcl-lang.io/script/install.sh -O - | /bin/bash
script:
- git checkout -B main
- cd deployment
# Image auto update
- /usr/local/kclvm/bin/kcl -d -O config.containers.flask_demo.image="$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA"
- git commit -am '[skip ci] image update to $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA'
- git push origin main
only:
- main
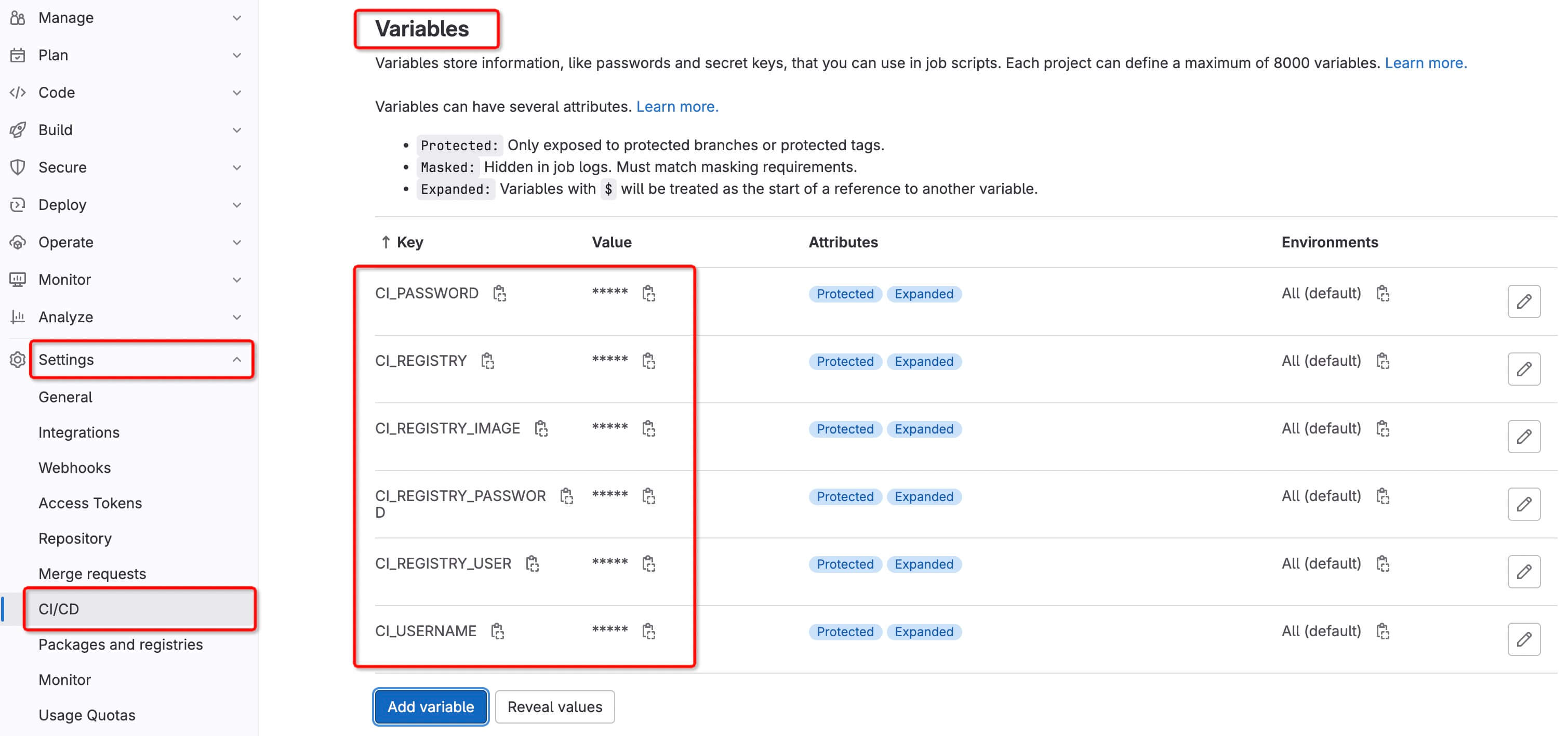
We need the workflow in the source code repository to automatically trigger the workflow in the deployment manifest repository. At this point, we need to config Settings -> CI/CD -> Variables including CI_REGISTRY, CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE, CI_REGISTRY_USER, CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD, CI_USERNAME and CI_PASSWORD and update application code to trigger automation build and deploy.
2. Commit the Application Code
After submitting in the flask-demo repository, Gitlab will automatically build a container image and push it to the Docker hub. It will also then trigger the Action of the flask-demo-kcl-manifest repository and modify the image value in the deployment manifest repository through KCL Automation API. Now let's create a submission in the flask-demo repository, and we can see that the code submission triggers the Gitlab CI process for the application repository Build -> Pipelines page.
3. Configuration Automatic Update
After the Gitlab CI process in the application repository is completed, an automatic update configuration CI will be triggered in the repository where the KCL configuration is stored and submitted to the main branch of the flask-demo repository.
- We can obtain the deployment manifest source code for compilation and validation
git checkout main && git pull && cd deploy && kcl
The output YAML is
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: flask_demo
labels:
app: flask_demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flask_demo
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: flask_demo
spec:
containers:
- name: flask_demo
image: "kcllang/flask_demo:6428cff4309afc8c1c40ad180bb9cfd82546be3e"
ports:
- protocol: TCP
containerPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask_demo
labels:
app: flask_demo
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: flask_demo
ports:
- port: 5000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5000
From the above configuration, it can be seen that the image of the resource is indeed automatically updated to the newly constructed image value. In addition, we can also use the Argo CD KCL plugin to automatically synchronize data from the Git repository and deploy the application to the Kubernetes cluster.
Summary
By integrating KCL and Gitlab CI, we can integrate the container build and delivery workflow by automatically updating the image values in the configuration, in order to achieve end-to-end application development process and improve R&D deployment efficiency.